Mars Colonization: Unlocking the Future Habitant
Explore the groundbreaking efforts in Mars colonization, from futuristic domed habitats to sustainable living on the red planet. Discover the challenges, innovations, and visionaries shaping humanity’s next frontier!
Mars Colonization: Unlocking the Future Habitant
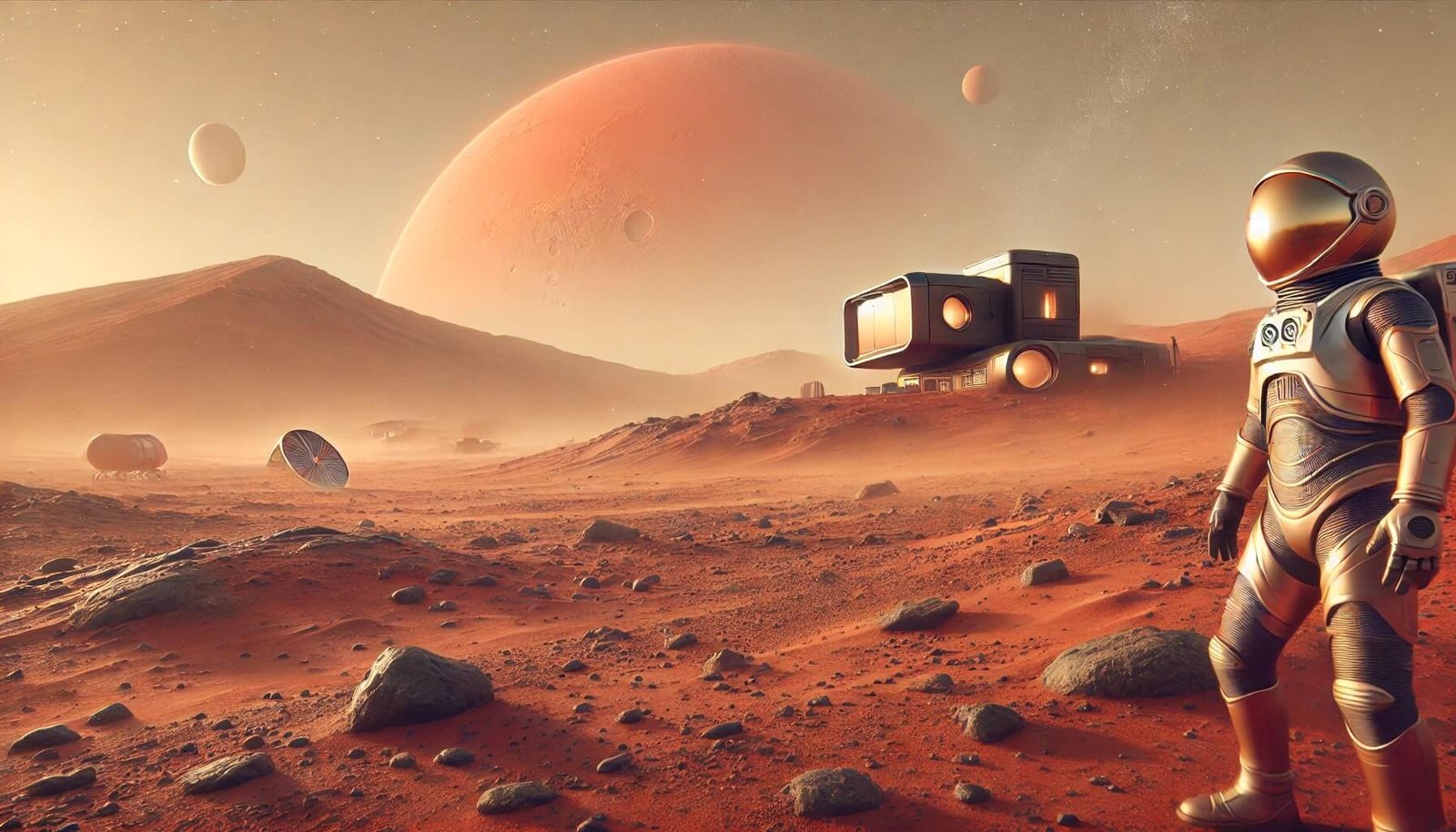
Humanity has always looked to the stars, but no celestial body has captured our imagination like Mars. As Earth’s closest neighbor with striking red terrain, Mars represents the ultimate frontier for exploration and survival. Over the past decade, scientists, engineers, and visionaries have made bold strides in turning the dream of Mars colonization into a potential reality. Here’s an in-depth look at the latest efforts, challenges, and future prospects for building a human presence on the Red Planet.
Why Mars? The Case for Colonization
Mars has long been considered the most viable planet for colonization. Its similarities to Earth—such as a 24.6-hour day and the presence of frozen water—make it a prime candidate for sustaining human life. Colonizing Mars isn’t just about exploration; it’s about ensuring humanity’s survival in the face of threats like climate change, resource depletion, or overpopulation on Earth.
In addition, Mars presents a unique chance for scientific research. The planet’s unique geology and history could provide answers about the early solar system and even clues about life beyond Earth. By establishing a permanent presence on Mars, humanity would also take its first steps toward becoming a truly interplanetary species.
Building Blocks of a Martian Colony
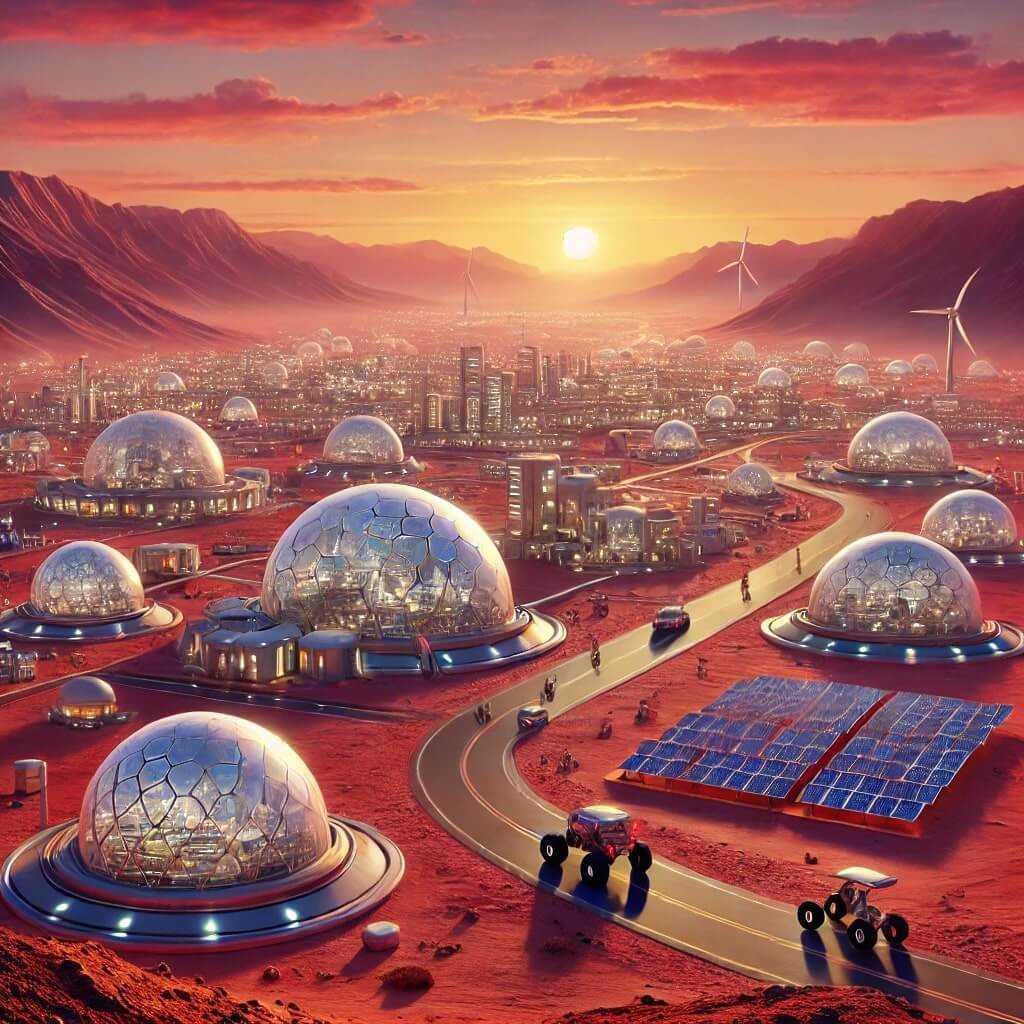

Domed Habitats: A Safe Haven
Building livable habitats is the first step in colonizing Mars. Futuristic domed structures made from materials like Martian regolith (soil) and advanced polymers are designed to withstand extreme conditions, including dust storms and radiation. These domes will provide pressurized environments where humans can breathe, grow food, and live comfortably.
The concept of 3D printing habitats on Mars using locally sourced materials is gaining traction. This innovative approach would minimize the need to transport heavy construction materials from Earth, significantly reducing costs.
Solar Panels for Energy
On Mars, solar energy will be the main power source. Panels designed to capture the weaker sunlight on the planet will fuel habitats, communication systems, and research equipment. The use of solar farms is a sustainable solution that aligns with Mars’ unique environment. Additionally, advancements in energy storage systems, such as high-capacity batteries, are crucial for ensuring power availability during the long Martian nights.
Water Extraction and Recycling
Access to water is crucial for any colony. NASA and private companies like SpaceX are developing methods to extract water from underground ice deposits and the atmosphere. Advanced recycling systems will ensure minimal water waste, supporting long-term habitation. Technologies such as electrolysis could also convert water into hydrogen and oxygen for fuel and breathing, further reducing dependence on Earth supplies.
The Role of SpaceX and Other Pioneers
Elon Musk’s SpaceX is leading the charge with its Starship spacecraft, designed to transport humans and cargo to Mars. Musk envisions a self-sustaining city on Mars by the 2050s, complete with homes, schools, and businesses.
SpaceX has already conducted successful tests of Starship prototypes, showcasing their ability to carry heavy payloads and return safely to Earth. Larger-scale missions are being made possible by these testing. Other organizations, like NASA and Blue Origin, are also playing pivotal roles in advancing technologies for interplanetary travel and habitation.
Collaboration is Key
While private companies like SpaceX are spearheading the effort, partnerships with government agencies and international organizations are vital. Collaborative missions ensure the pooling of resources, expertise, and funding, accelerating progress toward Mars colonization.
Mars!!
Mars, often referred to as the “Red Planet,” is the fourth planet from the Sun, known for its distinctive red color due to its iron oxide-rich surface. It is about half the size of Earth, with a diameter of 6,779 kilometers (4,212 miles), and is orbited by two small moons, Phobos and Deimos, believed to be captured asteroids. The planet has a thin atmosphere composed mainly of carbon dioxide, making it inhospitable for human life. Surface temperatures vary widely, ranging from -125°C (-195°F) near the poles to 20°C (68°F) at the equator during summer.
Overcoming Challenges on Mars
Colonizing Mars isn’t without its hurdles. Addressing these challenges is essential for the success of any mission:
Radiation Exposure
Mars lacks a magnetic field, leaving its surface exposed to harmful cosmic rays. Solutions include building underground shelters or using radiation-resistant materials for habitats. Some proposals even suggest using water as a radiation shield.
Low Temperatures
With an average surface temperature of -60°C (-80°F), heating habitats and maintaining crop growth pose significant challenges. Advanced insulation and greenhouse technology are critical innovations. Scientists are also exploring genetically modified crops that can thrive in harsh Martian conditions.
Transportation Costs
Sending supplies and personnel to Mars remains expensive. Innovations in rocket reusability and in-situ resource utilization (using local resources) are key to reducing costs. SpaceX’s Starship, with its fully reusable design, represents a significant leap in making interplanetary travel more affordable.
The Future of Mars Colonization
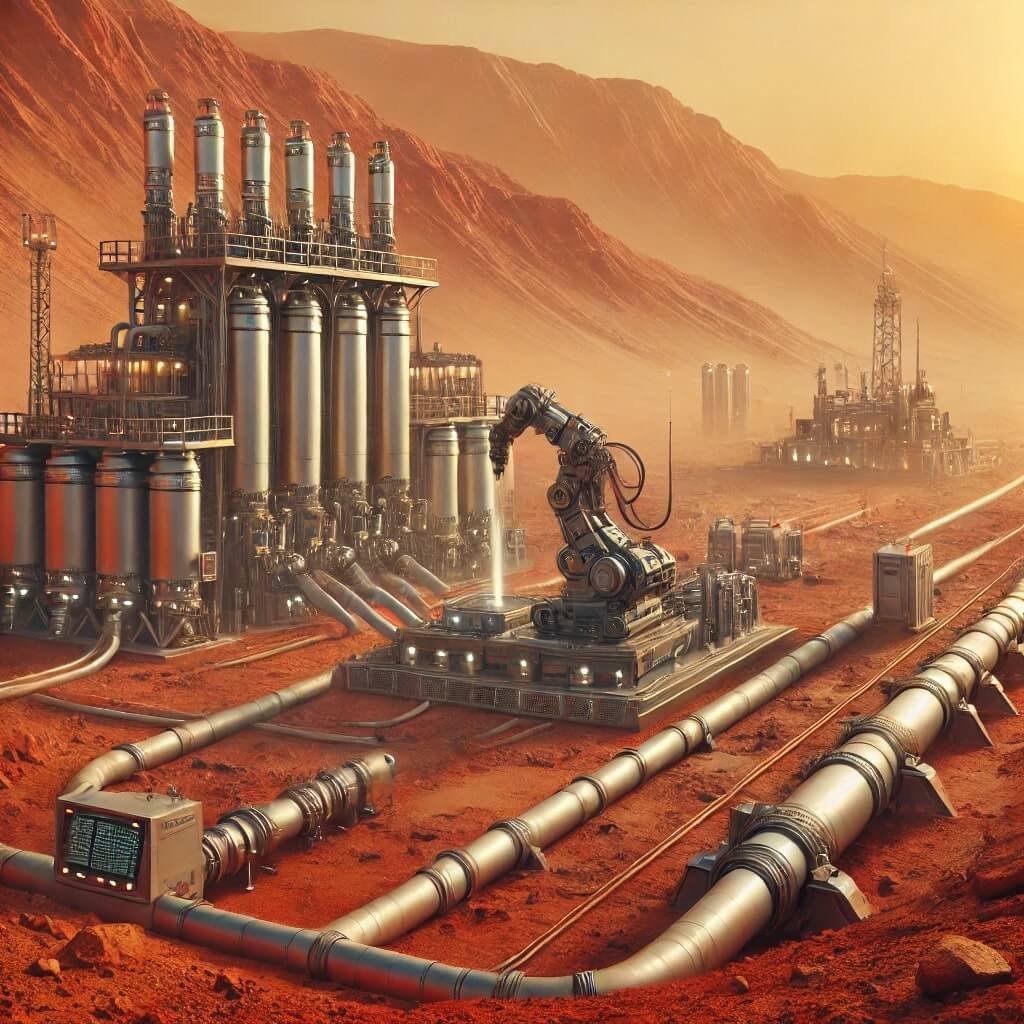

1. Sustainable Living
The goal is to create self-sustaining colonies where residents can grow food, generate power, and recycle resources without relying heavily on Earth. Innovations like vertical farming, 3D printing of tools, and energy-efficient systems are paving the way.
1. Sustainable Living
A colony on Mars offers opportunities for groundbreaking research. Scientists will study Mars’ geology, search for signs of ancient life, and test new technologies that could benefit Earth. For example, understanding how to grow crops in Martian soil could revolutionize agriculture on Earth.
3. Expanding the Space Economy
Mars colonization will drive industries like mining and manufacturing in space. Resources from Mars could support Earth-based industries or serve as raw materials for expanding human presence in the solar system. The development of a robust space economy will also create new job opportunities and economic growth.
Inspiring the Next Generation
Mars colonization isn’t just a technological challenge—it’s an inspiration. The idea of living on another planet sparks curiosity and innovation among students, scientists, and entrepreneurs worldwide. Governments and private companies are investing in educational programs to prepare future Martian settlers.
Films, books, and media also play a significant role in keeping Mars exploration in the public eye. Stories like “The Martian” and “For All Mankind” highlight the allure and challenges of interplanetary living, inspiring a global audience.
Final Thought: Fearlessly Venturing Where No One Has Before
No longer is the idea of colonising Mars limited to science fiction. With advancements in technology, bold leadership from companies like SpaceX, and a global commitment to exploration, humanity is on the cusp of becoming an interplanetary species.
Mars Colonization: Unlocking the Future Habitant
Humanity has always looked to the stars, but no celestial body has captured our imagination like Mars. As Earth’s closest neighbor with striking red terrain, Mars represents the ultimate frontier for exploration and survival. Over the past decade, scientists, engineers, and visionaries have made bold strides in turning the dream of Mars colonization into a potential reality. Here’s an in-depth look at the latest efforts, challenges, and future prospects for building a human presence on the Red Planet.
Why Mars? The Case for Colonization
Mars has long been considered the most viable planet for colonization. Its similarities to Earth—such as a 24.6-hour day and the presence of frozen water—make it a prime candidate for sustaining human life. Colonizing Mars isn’t just about exploration; it’s about ensuring humanity’s survival in the face of threats like climate change, resource depletion, or overpopulation on Earth.
In addition, Mars presents a unique chance for scientific research. The planet’s unique geology and history could provide answers about the early solar system and even clues about life beyond Earth. By establishing a permanent presence on Mars, humanity would also take its first steps toward becoming a truly interplanetary species.
Building Blocks of a Martian Colony

Water Extraction and Recycling
Access to water is crucial for any colony. NASA and private companies like SpaceX are developing methods to extract water from underground ice deposits and the atmosphere. Advanced recycling systems will ensure minimal water waste, supporting long-term habitation. Technologies such as electrolysis could also convert water into hydrogen and oxygen for fuel and breathing, further reducing dependence on Earth supplies.
Domed Habitats: A Safe Haven
Building livable habitats is the first step in colonizing Mars. Futuristic domed structures made from materials like Martian regolith (soil) and advanced polymers are designed to withstand extreme conditions, including dust storms and radiation. These domes will provide pressurized environments where humans can breathe, grow food, and live comfortably.
The concept of 3D printing habitats on Mars using locally sourced materials is gaining traction. This innovative approach would minimize the need to transport heavy construction materials from Earth, significantly reducing costs.
Solar Panels for Energy
On Mars, solar energy will be the main power source. Panels designed to capture the weaker sunlight on the planet will fuel habitats, communication systems, and research equipment. The use of solar farms is a sustainable solution that aligns with Mars’ unique environment. Additionally, advancements in energy storage systems, such as high-capacity batteries, are crucial for ensuring power availability during the long Martian nights.
The Role of SpaceX and Other Pioneers
Elon Musk’s SpaceX is leading the charge with its Starship spacecraft, designed to transport humans and cargo to Mars. Musk envisions a self-sustaining city on Mars by the 2050s, complete with homes, schools, and businesses.
SpaceX has already conducted successful tests of Starship prototypes, showcasing their ability to carry heavy payloads and return safely to Earth. Larger-scale missions are being made possible by these testing. Other organizations, like NASA and Blue Origin, are also playing pivotal roles in advancing technologies for interplanetary travel and habitation.
Collaboration is Key
While private companies like SpaceX are spearheading the effort, partnerships with government agencies and international organizations are vital. Collaborative missions ensure the pooling of resources, expertise, and funding, accelerating progress toward Mars colonization.
Mars!!
Mars, often referred to as the “Red Planet,” is the fourth planet from the Sun, known for its distinctive red color due to its iron oxide-rich surface. It is about half the size of Earth, with a diameter of 6,779 kilometers (4,212 miles), and is orbited by two small moons, Phobos and Deimos, believed to be captured asteroids. The planet has a thin atmosphere composed mainly of carbon dioxide, making it inhospitable for human life. Surface temperatures vary widely, ranging from -125°C (-195°F) near the poles to 20°C (68°F) at the equator during summer.
Overcoming Challenges on Mars
Colonizing Mars isn’t without its hurdles. Addressing these challenges is essential for the success of any mission:
Radiation Exposure
Mars lacks a magnetic field, leaving its surface exposed to harmful cosmic rays. Solutions include building underground shelters or using radiation-resistant materials for habitats. Some proposals even suggest using water as a radiation shield.
Low Temperatures
With an average surface temperature of -60°C (-80°F), heating habitats and maintaining crop growth pose significant challenges. Advanced insulation and greenhouse technology are critical innovations. Scientists are also exploring genetically modified crops that can thrive in harsh Martian conditions.
Transportation Costs
Sending supplies and personnel to Mars remains expensive. Innovations in rocket reusability and in-situ resource utilization (using local resources) are key to reducing costs. SpaceX’s Starship, with its fully reusable design, represents a significant leap in making interplanetary travel more affordable.
The Future of Mars Colonization

1. Sustainable Living
The goal is to create self-sustaining colonies where residents can grow food, generate power, and recycle resources without relying heavily on Earth. Innovations like vertical farming, 3D printing of tools, and energy-efficient systems are paving the way.
2. Scientific Discoveries
A colony on Mars offers opportunities for groundbreaking research. Scientists will study Mars’ geology, search for signs of ancient life, and test new technologies that could benefit Earth. For example, understanding how to grow crops in Martian soil could revolutionize agriculture on Earth.
3. Expanding the Space Economy
Mars colonization will drive industries like mining and manufacturing in space. Resources from Mars could support Earth-based industries or serve as raw materials for expanding human presence in the solar system. The development of a robust space economy will also create new job opportunities and economic growth.
Inspiring the Next Generation
Mars colonization isn’t just a technological challenge—it’s an inspiration. The idea of living on another planet sparks curiosity and innovation among students, scientists, and entrepreneurs worldwide. Governments and private companies are investing in educational programs to prepare future Martian settlers.
Films, books, and media also play a significant role in keeping Mars exploration in the public eye. Stories like “The Martian” and “For All Mankind” highlight the allure and challenges of interplanetary living, inspiring a global audience.
Final Thought: Fearlessly Venturing Where No One Has Before
No longer is the idea of colonising Mars limited to science fiction. With advancements in technology, bold leadership from companies like SpaceX, and a global commitment to exploration, humanity is on the cusp of becoming an interplanetary species.
Call to Action:
Want to stay updated on the latest space innovations? Bookmark this page and join with us for exclusive insights into the world of private space exploration! Mail us this email.