Who Was Imhotep?
Imhotep is widely regarded as one of the most important figures in ancient Egypt, living around 2650 BCE during the reign of Pharaoh Djoser. He is known for his multifaceted genius as an architect, physician, high priest, and scribe.
His contributions to architecture, particularly the design of the Step Pyramid of Djoser at Saqqara, revolutionized Egyptian burial practices. As a medical practitioner, he earned the title of the father of medicine for his pioneering work in surgery, herbal medicine, and diagnostics. His influence stretched across the Old Kingdom, Middle Kingdom, and even into the New Kingdom of Egypt.
Over time, his legacy grew to the point where he was deified as a God of Medicine and Healing. His legacy remains a significant part of Egyptian history and culture, and his innovations in architecture and medicine continue to be studied today.
Table of Contents
Early Life and Background
Despite his monumental achievements, little is known about his early life. He is believed to have come from a modest background but quickly rose to prominence as the chief architect and advisor to Pharaoh Djoser during Egypt’s Third Dynasty. His rise to power is remarkable, as most high-ranking officials in ancient Egypt were members of the royal family or nobility. His name, which means “the one who comes in peace,” reflected his peaceful nature and intellectual approach to his work in medicine, architecture, and theology.
He was a polymath whose skills transcended many disciplines, making him one of the most revered figures in ancient Egyptian history.
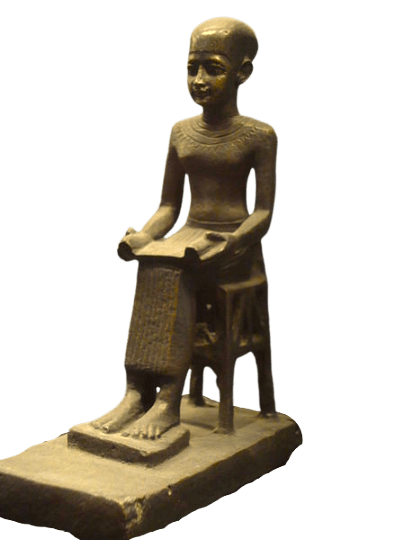

Fig: Imhotep (between 332 and 30 BC)
Architectural Genius: The Step Pyramid of Djoser
His most famous architectural achievement is the Step Pyramid of Djoser, which is considered the world’s first monumental stone structure. This pyramid, located in Saqqara, broke from traditional Egyptian burial structures, known as mastabas, by incorporating six stacked mastabas, creating a stepped design. This innovation not only marked a shift in architectural style but also in the spiritual and ceremonial aspects of Egyptian culture.
The Step Pyramid stands at 62 meters (203 feet) tall and was surrounded by a complex of courtyards, temples, and shrines. It marked the beginning of pyramid construction in Egypt, influencing the later construction of the Great Pyramids of Giza.

Fig: Step Pyramid of Djoser in Saqqara, designed by Imhotep, the first monumental stone structure in Egyptt
The Father of Medicine
In addition to his architectural feats, he is considered the first recorded physician in history. His medical practices, documented in the Edwin Smith Papyrus, are still respected for their systematic approach to diagnoses and treatments. His medical work focused primarily on treating wounds, setting fractures, and using herbal remedies. His methods were advanced for his time, and he emphasized the importance of cleanliness in treating wounds—an idea far ahead of its time.
- Surgical Techniques: His texts detail several surgical techniques, including the treatment of broken bones and dislocated joints. His methods of surgery, particularly for trauma care, were groundbreaking.
- Diagnosis and Treatment: His medical treatises demonstrated a logical approach to diagnosis and treatment. His medical philosophy, based on observation and evidence, was revolutionary in a time when much of medicine relied on superstition.
- Herbal Remedies: His was a pioneer in the use of plant-based treatments. His knowledge of herbs and their medicinal properties influenced the development of early pharmacology.

Fig: Ancient Egyptian Medical tools
Influence in Ancient Egypt
Imhotep’s influence extended beyond architecture and medicine. He was a revered figure throughout Egypt’s long history, from the Old Kingdom to the New Kingdom. His ideas continued to influence Egyptian society for centuries
Impact on the Old, Middle, and New Kingdoms
Fig: Ancient Egyptian Map BC 3000 AD 640
His contributions laid the foundation for many architectural advancements during Egypt’s Old Kingdom. His pyramid design influenced subsequent pyramid builders, including those of the Middle Kingdom and New Kingdom, where pharaohs like Ramses continued to build grand monuments and temples.
During the Middle Kingdom (c. 2050 BCE – 1710 BCE), his architectural innovations were still being employed, and his medical texts were used as a basis for further development in the field of medicine.
In the New Kingdom (c. 1550 BCE – 1070 BCE), His status grew even further, culminating in his eventual deification.
Ramses and Imhotep’s Legacy
Ramses II, also known as Ramses the Great, reigned during the New Kingdom and built some of the most iconic monuments in Egypt. Although he lived centuries after Imhotep, Ramses continued to build on the architectural foundations that Imhotep had laid during the Old Kingdom. Ramses’ temples and colossal statues reflect the same spirit of grandeur that Imhotep brought to Djoser’s Step Pyramid.
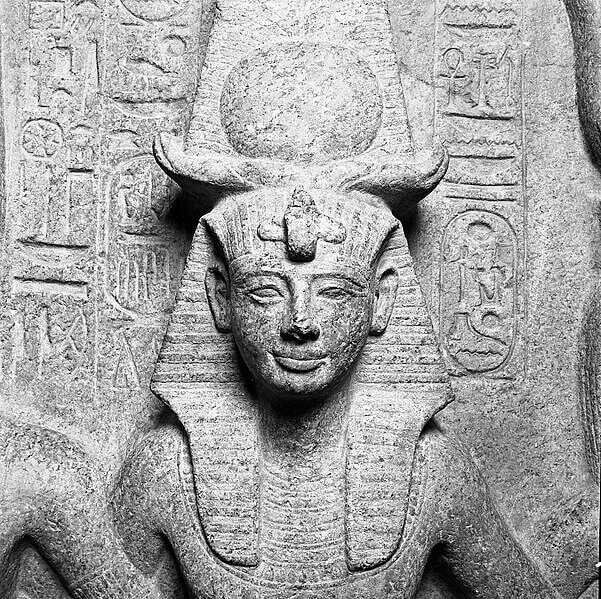

Fig: Statue of Ramses II
Religious Role: High Priest of Heliopolis
Imhotep also served as a high priest at Heliopolis, one of Egypt’s most important religious centers. His duties as a high priest placed him at the heart of Egyptian religious life, where he oversaw rituals, temple maintenance, and ceremonies dedicated to the worship of Ra, the sun god. His role in religion allowed him to bridge the gap between science, architecture, and spirituality, blending the fields in ways that shaped Egypt’s cultural development.
Imhotep’s Deification and Legacy
Centuries after his death, Imhotep was deified as a God of Medicine and Healing. His cult was especially popular during the Ptolemaic Period (332–30 BCE), and temples were built in his honor. Imhotep’s image as a healer and wise man transcended his time, and his influence was recognized not only in Egypt but also by Greek scholars, including Hippocrates and Galen, who credited him as a forer.


Fig: 1- Canopic jar, 2- Model Funerary Boat, 3- Book of the Dead of the Priest of Horus, 4- Plaque inscribed with the name and titles.




knowledge able post.
Excellent post. I was checking continuously this blog and
I’m inspired! Extremely helpul info pwrticularly the last part :
) I take care of such imfo a lot. I was seeking this certain information for a
long time. Thank you and good luck. https://evolution.org.ua/
Great goods from you, man. I’ve understand your stuff previous to and you are just too great. I actually like what you’ve acquired here, really like what you are stating and the way in which you say it. You make it entertaining and you still take care of to keep it wise. I can’t wait to read much more from you. This is really a tremendous site.
Hi, There’s no doubt that your web site could possibly be having broaser
compatibility issues. Whenever I take a look at your blog in Safari, it looks fine however whwn opening iin IE, it has some overlapping issues.
I simply wanted to provide you with a quick heads up!
Besides that, wondereful blog! https://www.remotehub.com/rosa.brown