
History of Ancient Egypt: Gods, Hieroglyphs, and Civilizations
Discover the rich history of ancient Egypt, its gods, hieroglyphs, symbols, and artifacts. Learn how this remarkable civilization shaped the world with its culture, innovation, and artistry.
Exploring the Fascinating History of Ancient Egypt
The history of ancient Egypt is a story of grandeur, innovation, and spirituality. Known as one of the world’s earliest and most enduring civilizations, ancient Egypt thrived along the fertile banks of the Nile River for thousands of years. Its complex belief systems, imposing architecture, and rich culture have made a lasting impression on the world. This article explores the fascinating journey of ancient Egypt, delving into its gods, hieroglyphs, symbols, and artifacts that continue to captivate humanity.
The Origins of Ancient Egyptian Civilization
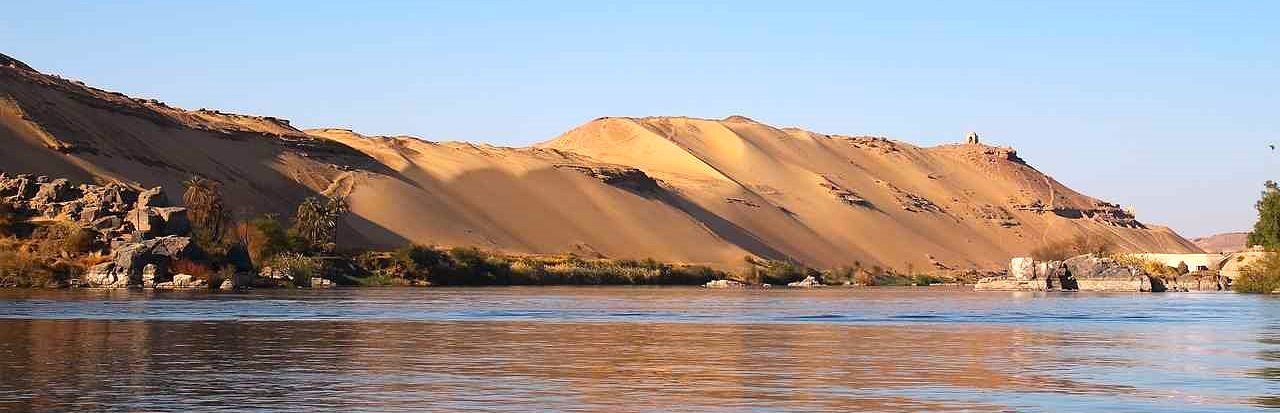
A Land Shaped by the Nile
The first pharaoh, King Narmer, brought Upper and Lower Egypt together about 3100 BCE, marking the beginning of ancient Egypt. Because of the Nile River’s consistent flooding, which produced rich soil for farming, this civilization flourished there. Known as “The Gift of the Nile,” the river supported the development of a complex society with a stable food supply and advanced trade systems.
The Nile’s importance extended beyond agriculture—it was also a key transportation route, connecting different regions of Egypt and facilitating trade with neighboring civilizations such as Nubia and Mesopotamia. This geographic advantage played a vital role in Egypt’s rise as a powerful and enduring civilization.

The Structure of Egyptian Society
Ancient Egypt was a highly stratified society with the pharaoh at the top as both a political and religious leader. The base of the social pyramid was made up of farmers and laborers, while the pharaoh was surrounded by scribes, artisans, priests, and nobles.
The belief in divine kingship elevated the pharaoh’s status, making him the intermediary between the gods and the people. This hierarchical structure ensured the smooth functioning of a vast empire, enabling monumental architectural projects like the pyramids and temples.
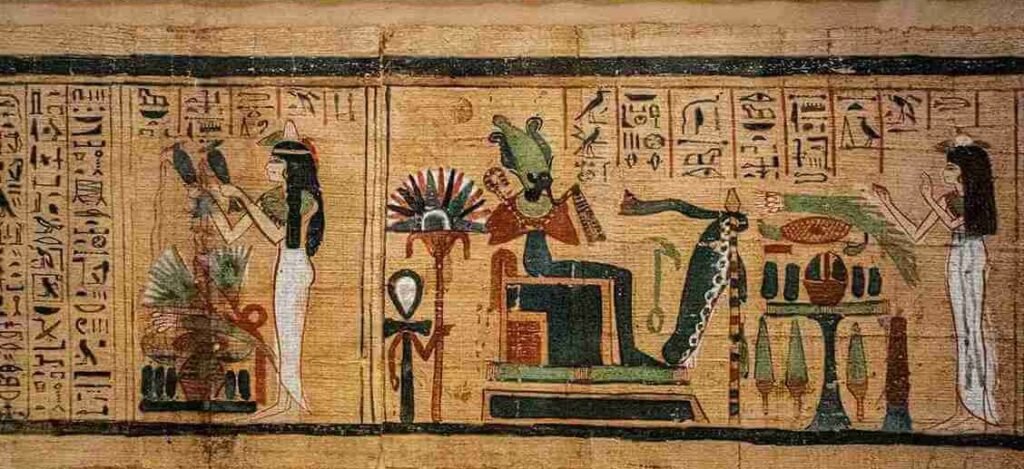
Religion and the Egyptian Gods
The spiritual beliefs of ancient Egypt revolved around a complex pantheon of gods and goddesses, each representing natural forces or aspects of life. Among the most venerated Egyptian deities are:
Ra: The sun god and creator of life, central to Egyptian mythology.
Osiris: The god of rebirth, the afterlife, and resurrection.
Isis: The goddess of magic and motherhood, worshipped for her protective powers.
Anubis: The deity of mummification who guides souls into the afterlife.
Temples dedicated to these deities were centers of religious, political, and economic activity. Festivals honoring the gods, such as the “Opet Festival” in Thebes, brought communities together in celebration of their shared faith.
Learn More About Microplastic Pollution Solutions: Revolutionizing Clean Ocean
Galaxies Mystery
Galaxies are among the universe’s most mysterious and awe-inspiring structures, home to billions of stars, planets, and other celestial objects. One of the greatest enigmas is the presence of dark matter, an invisible substance that holds galaxies together through its gravitational pull. Within their cores, supermassive black holes lurk, consuming matter and emitting powerful jets of energy, shaping the galaxy’s evolution. Some galaxies defy explanation, such as those with almost no dark matter or stars moving at unimaginable speeds. Others, like quasars, shine with incredible luminosity, powered by ancient black holes. Galaxies are not only cosmic wonders but also hold the secrets to understanding the universe’s past, present, and future.
Symbols and Artifacts: A Window into Egyptian Life
Symbols played a central role in Egyptian culture, representing concepts like power, protection, and eternity. Among the most recognizable Egyptian symbols are:
The Ankh: Often seen in the hands of gods, this emblem represents life and immortality.
The Eye of Horus: A protective symbol warding off evil spirits.
Ancient Egyptian life is revealed through artifacts including jewelry, utensils, and pottery. Magnificent treasures, like King Tutankhamun’s golden mask and the intricate canopic jars used in mummification, showcase the artistry and craftsmanship of this civilization. These Egyptian artifacts are invaluable in understanding their culture, technology, and beliefs.
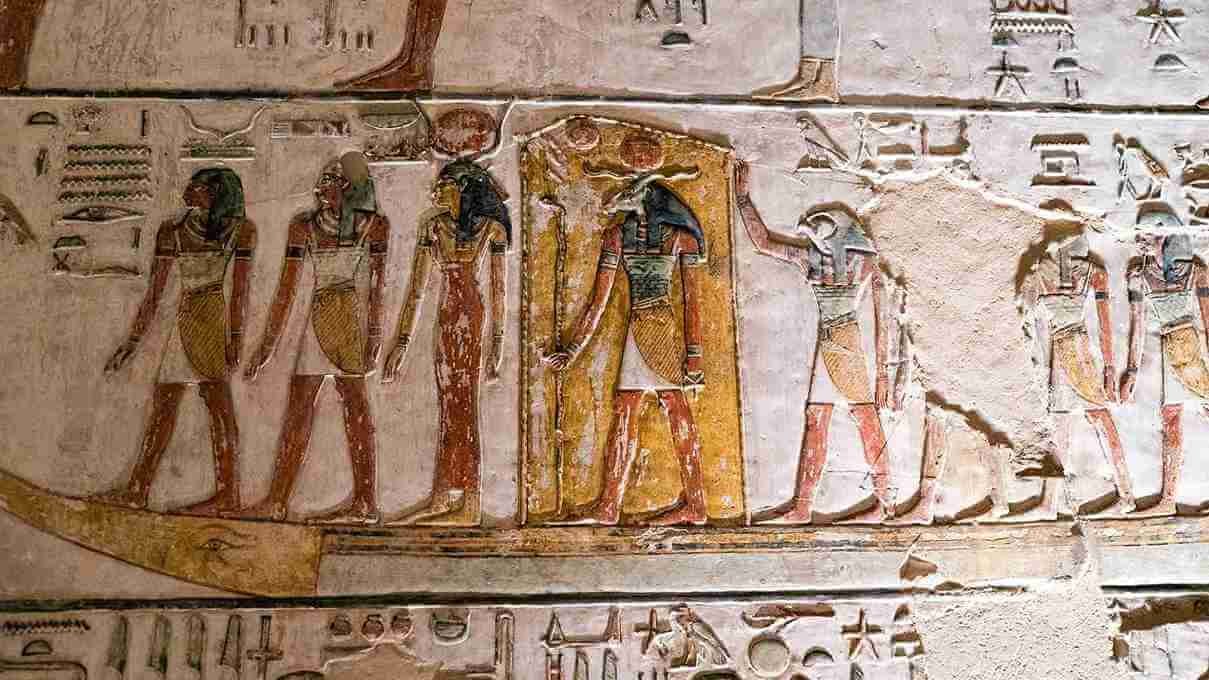
Egyptian Hieroglyphs: The Art of Writing
The Evolution of Hieroglyphs
The ancient Egyptians developed a unique writing system known as Egyptian hieroglyphs, consisting of over 700 symbols. These visual characters were primarily used in religious texts, official records, and monumental inscriptions.
The discovery of the Rosetta Stone in 1799 was instrumental in deciphering these hieroglyphs, unlocking a treasure trove of historical information about ancient Egypt’s administration, religion, and daily life.
Hieroglyphs in Art and Architecture
Hieroglyphs were not only functional but also artistic. They adorned temple walls, tombs, and papyrus scrolls, often blending seamlessly with intricate carvings and paintings. They continue to be among the most identifiable representations of ancient Egyptian culture today.


Ancient Egyptian Jewelry and Writing Systems
Jewelry as Status and Protection
Ancient Egyptian jewelry served a symbolic purpose in addition to being ornamental. Made from gold, turquoise, lapis lazuli, and other precious materials, these pieces often featured protective symbols like the ankh and scarab. Both men and women wore jewelry to show off their wealth, prestige, and spiritual defense.
The Development of Writing Systems
While hieroglyphs were the primary writing system for monumental inscriptions, Egyptians also developed the hieratic and demotic scripts for everyday communication. These simplified writing systems were used for administrative tasks, trade, and personal correspondence, showcasing the practical side of Egyptian ingenuity.
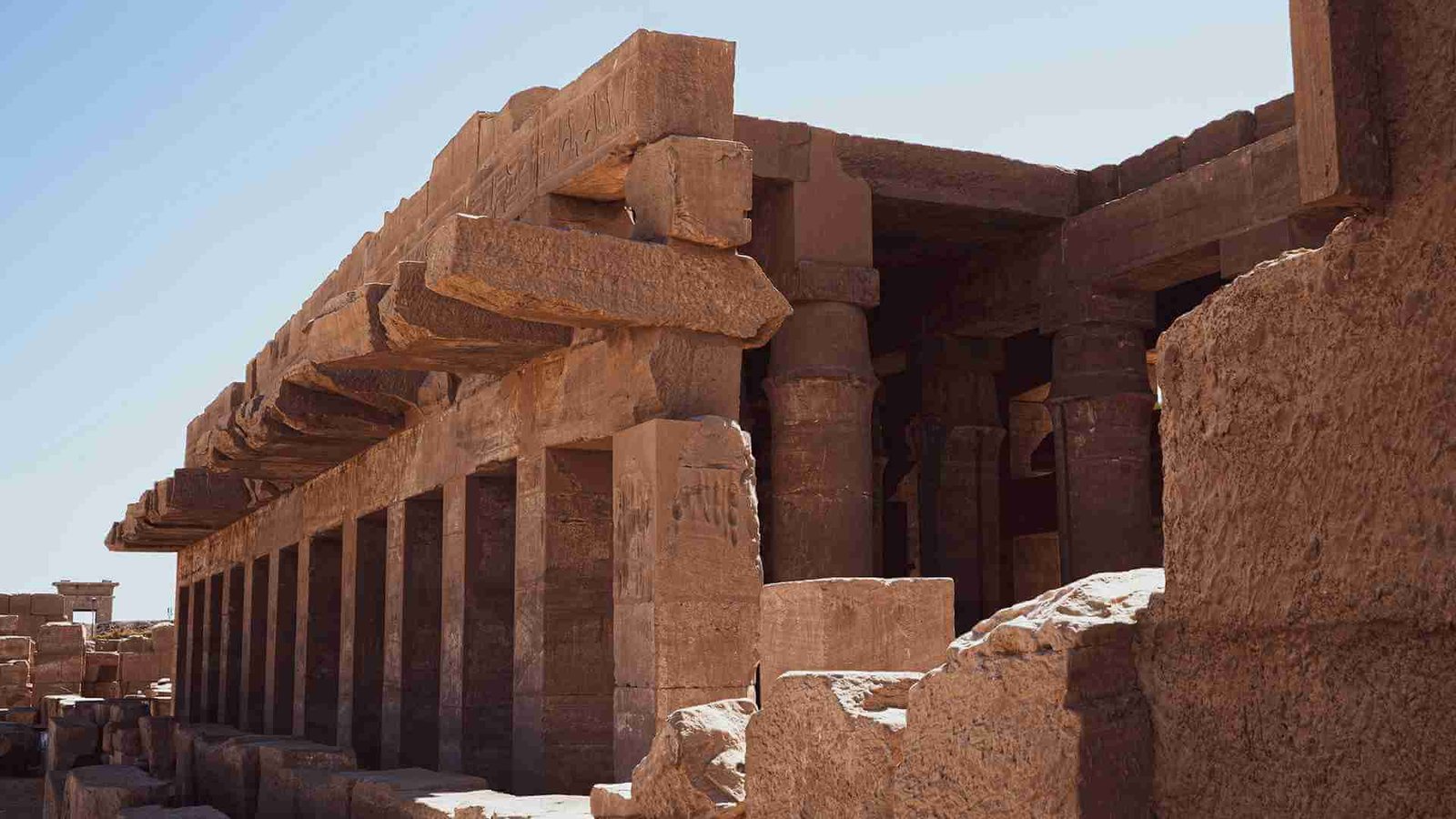
Architectural Marvels of Ancient Egypt
The monumental architecture of ancient Egypt reflects its cultural and religious priorities. The Great Pyramid of Giza, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, was built as a tomb for Pharaoh Khufu, showcasing the Egyptians’ engineering prowess.
Temples such as Karnak and Abu Simbel were designed to honor the gods and demonstrate the pharaoh’s divine authority. These structures were adorned with intricate carvings, statues, and hieroglyphs, making them enduring symbols of Egypt’s grandeur.
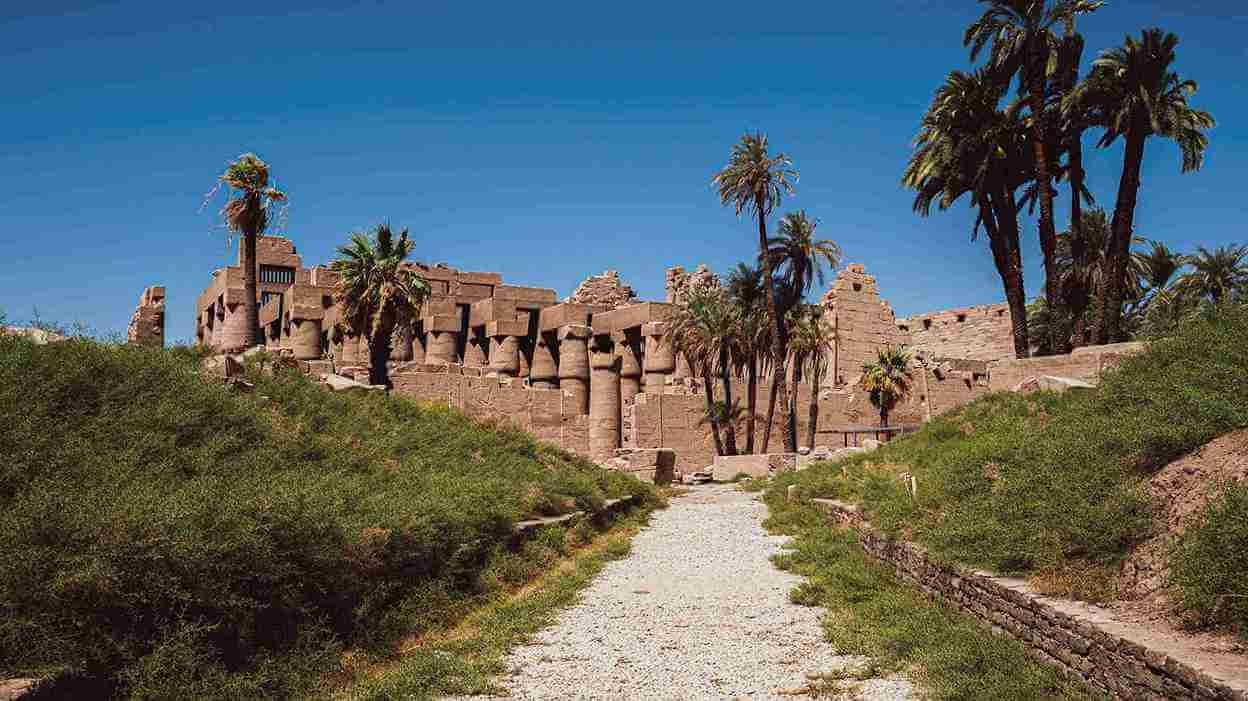


Legacy and Influence of Ancient Egypt
The history of ancient Egypt continues to inspire the modern world. From advancements in medicine and astronomy to architectural innovations, Egypt’s contributions have left a lasting legacy.
The belief in an eternal afterlife influenced their burial practices, leading to the preservation of mummies and tombs that provide invaluable insights into their lives. Modern archaeology continues to uncover new findings, shedding light on this remarkable civilization’s complexity and achievements.
Conclusion: An Enduring Civilization
The history of ancient Egypt is a testament to humanity’s creativity, resilience, and quest for meaning. Its gods, hieroglyphs, symbols, and artifacts offer a window into a world that thrived thousands of years ago yet continues to captivate us. By exploring its rich heritage, we connect with one of history’s greatest civilizations and draw lessons that remain relevant today.













Some really nice and useful info on this site, also I think the design has got wonderful features.