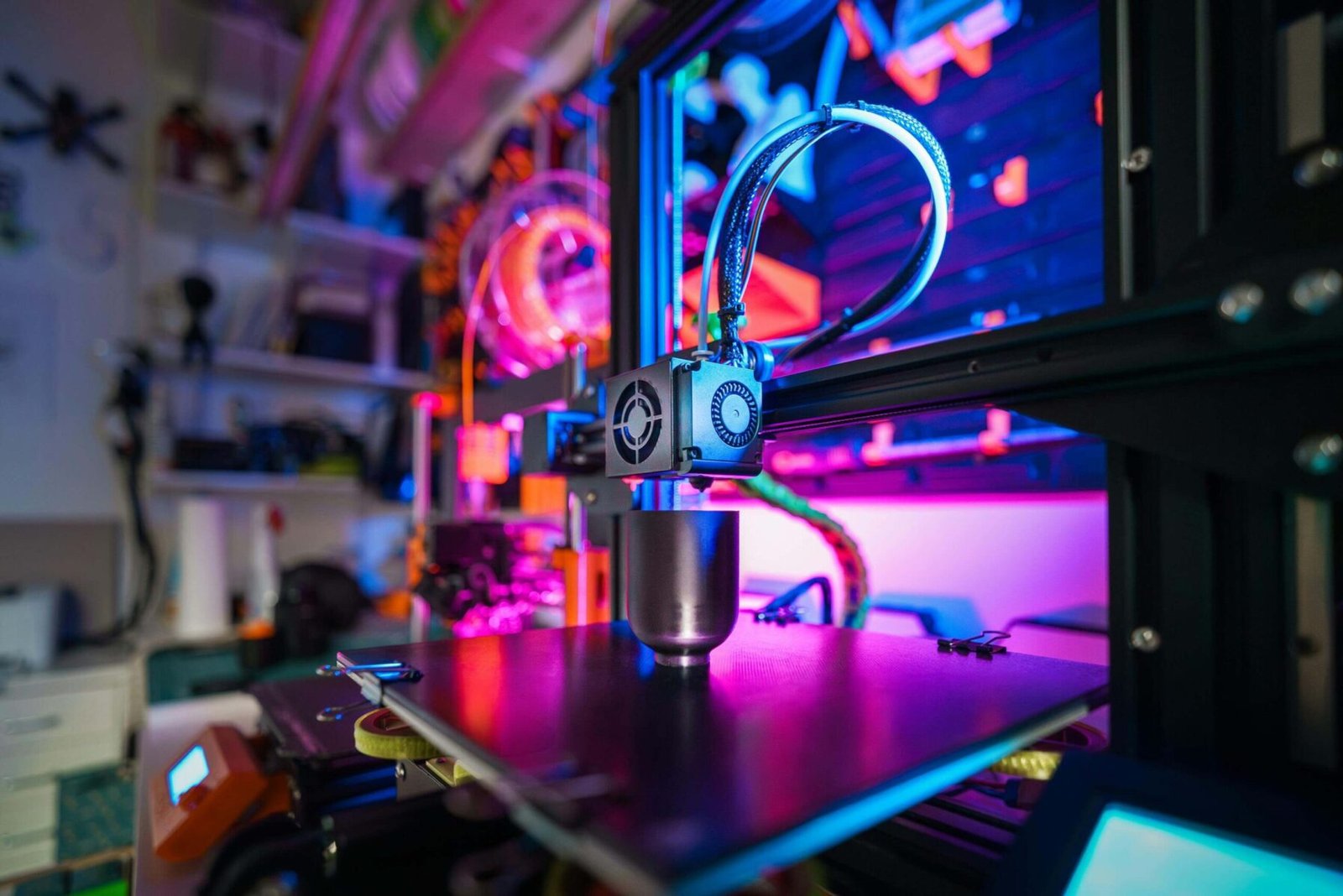

Understanding 3D printer and its impact on 3D printing
Learn about the revolutionary potential of 3D printing, including its industrial applications, novel materials, and how to get started, as well as the printers’ adaptability.
- December 6, 2024
- 7:40 pm
3D Printing Revolution: Exploring 3D Printers, Materials, and Industry Applications
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has redefined how products are designed, prototyped, and manufactured. This transformative technology, powered by advanced 3D printers, enables the creation of complex, customized, and durable objects layer by layer. With applications in industries like healthcare, aerospace, and automotive, 3D printing has become a critical innovation in modern manufacturing. We’ll examine the foundations of 3D printing in this post, along with its materials, advantages, and developing industrial uses.
What is 3D Printing?
At its core, 3D printing is the process of creating three-dimensional objects from a digital model. 3D printing creates things layer by layer, in contrast to traditional subtractive manufacturing, which shapes an object by removing material. This additive approach minimizes waste and allows for unprecedented design freedom.
The technology employs 3D printers to deposit materials like plastics, metals, and resins. With advancements in the field, industrial 3D printers can now produce large-scale parts, lightweight components, and even intricate medical devices with exceptional precision.

The Technology Behind 3D Printers
Modern 3D printers use various methods to create objects, each suited to specific applications:
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): Ideal for beginners and hobbyists, this method melts thermoplastics like PLA and ABS to create objects layer by layer.
- Stereolithography (SLA): Utilizes lasers to cure liquid resin into solid parts, known for its high resolution and smooth finishes.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): Fuses powdered materials, including metals, to create durable and lightweight components.
The versatility of these technologies makes 3D printing accessible for a range of users, from DIY enthusiasts to large-scale 3D printing companies.
Galaxies Mystery
Galaxies are among the universe’s most mysterious and awe-inspiring structures, home to billions of stars, planets, and other celestial objects. One of the greatest enigmas is the presence of dark matter, an invisible substance that holds galaxies together through its gravitational pull. Within their cores, supermassive black holes lurk, consuming matter and emitting powerful jets of energy, shaping the galaxy’s evolution. Some galaxies defy explanation, such as those with almost no dark matter or stars moving at unimaginable speeds. Others, like quasars, shine with incredible luminosity, powered by ancient black holes. Galaxies are not only cosmic wonders but also hold the secrets to understanding the universe’s past, present, and future.
Materials Used in 3D Printing
3D printing is renowned for its ability to use a wide variety of materials, catering to diverse needs:
- Plastics: Materials like PLA, ABS, and PETG are widely used due to their affordability and ease of use, especially in desktop 3D printers.
- Metals: Metal 3D printers utilize aluminum, titanium, and steel for aerospace and automotive applications where strength and durability are critical.
- Resins: Often used in SLA printing for jewelry and dentistry molds, resins are perfect for detailed models.
- Composite Materials: Innovations like carbon fiber filaments combine the strength of metal with the flexibility of plastic.
The variety of 3D printing materials ensures compatibility with industries requiring precision, strength, and customization.

Applications of 3D Printing
The versatility of 3D printing has revolutionized several industries:
Healthcare: From prosthetics to surgical implants, 3D printing allows for the creation of patient-specific medical devices.
Aerospace: Lightweight components printed with industrial 3D printers enhance fuel efficiency in aircraft and spacecraft.
Automotive: Prototyping parts for vehicles saves time and reduces production costs.
Education: Schools and universities utilize 3D printers to teach engineering, design, and problem-solving skills.
Consumer Goods: Companies craft custom products, from shoes to furniture, using additive manufacturing.
The adaptability of 3D printing technology is paving the way for innovation across these sectors.
Benefits of 3D Printing
The rise of 3D printing companies highlights the benefits of this technology:
- Customization: Products can be tailored to specific needs, from bespoke prosthetics to custom car parts.
- Cost Efficiency: Prototyping with 3D printers eliminates the need for expensive molds and tooling.
- Speed: Rapid prototyping accelerates product development cycles.
- Sustainability: Compared to conventional techniques, additive manufacturing produces less waste.
These benefits make 3D printing an essential tool for industries seeking efficiency and innovation.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While promising, 3D printing faces certain challenges:
- Cost of Equipment: High-end industrial 3D printers and materials remain expensive.
- Speed Limitations: Large-scale production can be slower than traditional manufacturing methods.
- Material Diversity: Not all materials are compatible with current technologies.
Notwithstanding these obstacles, 3D printing appears to have a promising future. Emerging trends include carbon fiber 3D printing, bioprinting for medical applications, and the development of faster, more cost-effective 3D printers.

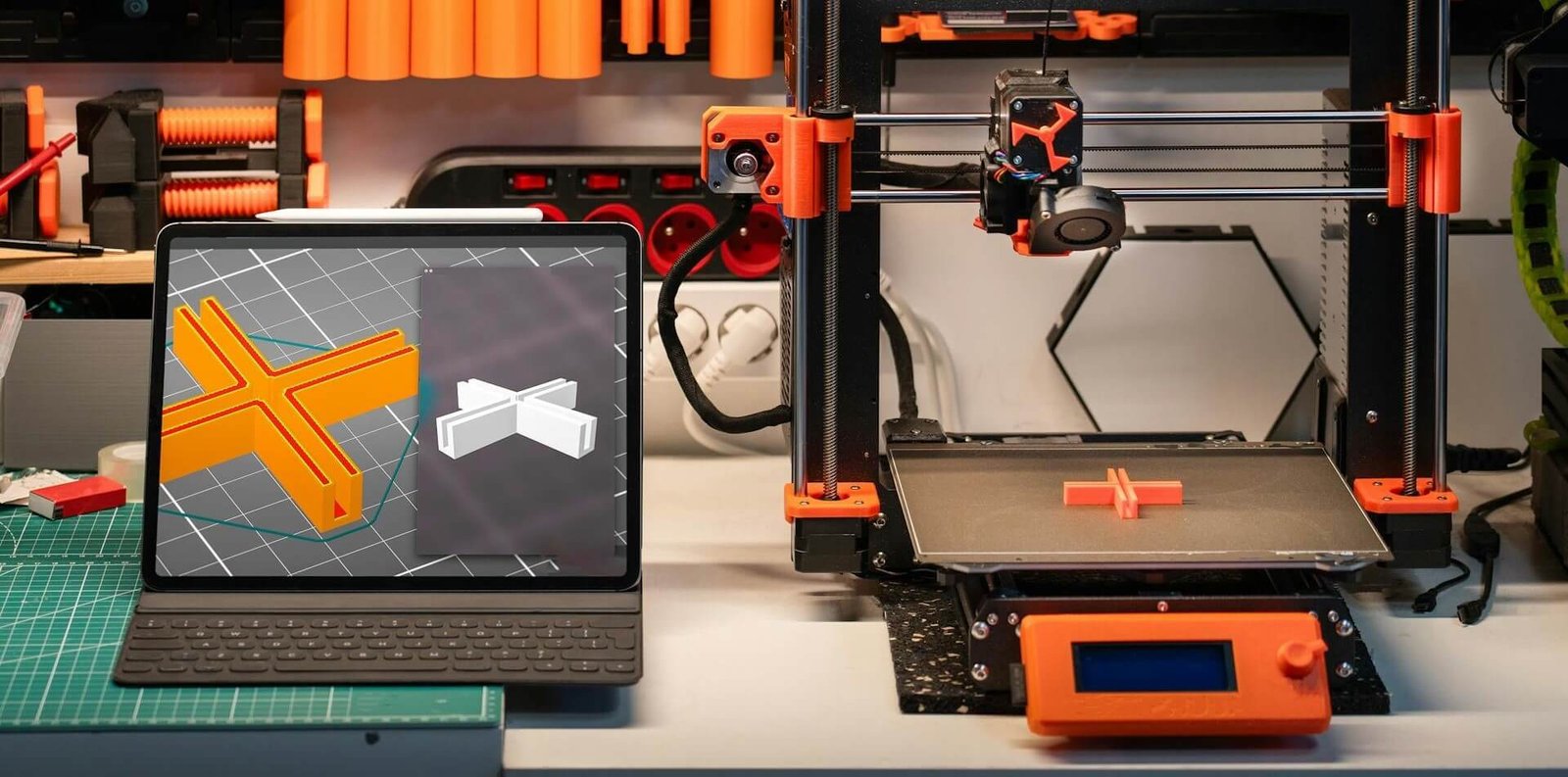
Long-Tail Insight: How to Make 3D Models for Printing
One of the most important steps in the 3D printing process is making 3D models. Using computer-aided design (CAD) software, designers can craft intricate models tailored to their needs. Tools like Blender, Tinkercad, and Fusion 360 are popular for creating models that can then be sliced into layers compatible with 3D printers. Gaining proficiency in this area will enable 3D printing technology to reach its maximum potential.
Long-Tail Insight: How to Make 3D Models for Printing
One of the most important steps in the 3D printing process is making 3D models. Using computer-aided design (CAD) software, designers can craft intricate models tailored to their needs. Tools like Blender, Tinkercad, and Fusion 360 are popular for creating models that can then be sliced into layers compatible with 3D printers. Gaining proficiency in this area will enable 3D printing technology to reach its maximum potential.
Conclusion: The Revolution Continues
The evolution of 3D printing is a testament to human ingenuity and the drive to innovate. From humble beginnings to complex industrial applications, technology has transformed how we create, design, and manufacture. The potential is limitless as 3D printers, materials, and applications develop further. Whether you’re a hobbyist, engineer, or industry leader, 3D printing offers tools to bring your ideas to life.















Deference to op, some superb selective information.